
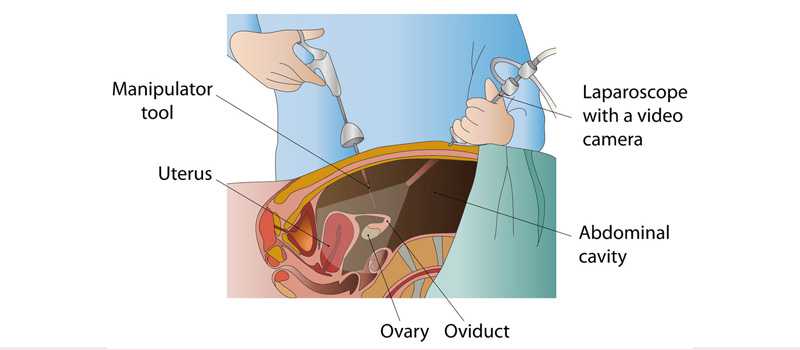
Laparoscopy, also known as key hole surgery, is a surgical procedure used to
examine the organs inside the abdomen. It’s a low-risk, minimally invasive
procedure that requires only small incisions.
Laparoscopy uses an instrument called a laparoscope to look at the
abdominal organs. A laparoscope is a long, thin tube with a high-intensity light
and a high-resolution camera at the front. The instrument is inserted through
an incision in the abdominal wall. As it moves along, the camera sends
images to a video monitor.
Laparoscopy allows surgeon to see inside abdomen in real time, without open
surgery.
Working this way has several advantages compared with traditional surgery. Because it involves less cutting:
• You have smaller scars.
• You get discharge quicker.
• You'll feel less pain while the scars heal, and they heal quicker.
• You get back to your normal activities sooner.
• You may have less internal scarring.
With traditional methods, you might spend 4 days or more in the hospital for open surgery, and your total recovery might take 4 to 8 weeks. If you have laparoscopic surgery, you might stay only 2 nights in the hospital and recover in 2 or 3 weeks.
Common procedures performed are:
1- DIAGNOSTIC LAPAROSCOPY
2- Laparoscopic adhesiolysis
3- Endometriosis fulguration
4-Myomectomy (fibroid removal)
5- Tubal ligation (TT)
6-Ovarian drilling for PCOS
7- Twisted ovarian cyst
8-Ovarian cyst removal
9-Tubal ligation
10- Tubal ectopic surgery
11- Tubo-ovarian masses
Tubal ligation is surgery to close a woman's fallopian tubes. (It is sometimes called "tying the tubes.") The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. A woman who has this surgery can no longer get pregnant.
Description
Tubal ligation is done in a hospital through an incision in abdomen or
laparoscopically.
The procedure takes about 30 minutes.
• Surgeon will make 1 or 2 small surgical cuts in your belly. Most often, they are around the belly button. Gas may be pumped into your belly to expand it. This helps your surgeon see your uterus and fallopian tubes.
• A narrow tube with a tiny camera on the end (laparoscope) is inserted into your belly. Instruments to block off your tubes will be inserted through the laparoscope or through a separate small cut.
• The tubes are either burned shut (cauterized) or clamped off with a small clip
or ring (band).
Tubal ligation can also be done right after you have a baby through a small
cut in the navel. It can also be done during a C-section.
Tubal Ligation, or tying of the tubes as it is more commonly referred to, is the most popular form of birth control the world over, and involves closing or blocking the fallopian tubes. However, you could have a change of heart later. In such a situation, you would need a Tubal Recanalisation / Reversal procedure to unblock your fallopian tube for passage of the sperm and the ovum.
What happens during the procedure?
A Tubal Recanalisation is done via laparoscopy or laparotomy to minimise risk of injury. During the procedure, the specialist places a speculum in the vagina and passes a catheter through the cervix into the uterus. The block is identified using a laparoscope or using a liquid contrast agent that is injected through the catheter. Once the block is identified, it is removed using a small catheter that is threaded through the previous catheter.
You could have minimal bleeding for a few days after the recanalisation procedure. However, of you experience pain, cramps, fever or abnormal discharge, see our specialist immediately.
Although microsurgical reversal completely reverses the tubal ligation, other factors such as duration of sterilisation, the technique used, and the length of the tube that remains after the reversal come in to play in deciding pregnancy rate.
The surgical removal of fibroids, which are tumours that grown within the muscle of the uterus, is called Myomectomy. The tumours can vary in size and number, and maybe the cause of long standing infertility or miscarriages, depending on their location. The procedure removes the tumours safely and improves chances of pregnancy.
we offer Hysteroscopic Myomectomy, Laparoscopic Myomectomy and Laparotomy-Abdominal Myomectomy depending on the number of fibroids to be removed, their location and size.
What happens during the procedure?
During a Hysteroscopic Myomectomy, we remove the fibroids through the
cervix. Although it is done under general anaesthesia, no incision is made.
You will be given a course of estrogen after the surgery to promote regrowth
of the uterine lining. Recommended Hospital Stay: Half a day and Recovery
time: 5-6 days.
In a Laparoscopic Myomectomy, the tumours are removed through a tiny
incision, under general anaesthesia. The recommended hospital stay is 1-2
days and recovery time is about 1 -2 weeks.
An Abdominal Myomectomy is an open surgery where the fibroids are
removed via an incision in the abdomen, through a laparotomy. We recommend this method when you have multiple fibroids that are larger than 10cms. The surgery, which is performed under general anaesthesia, takes
about 2 hours. The recommended hospital stay is 3 - 4 days and the recovery
time is about 4-6 weeks.
Ovarian cysts are fluid filled growths of the ovaries and can occur across all
age groups.
There are three kinds of cysts: functional, neoplastic – which may or may not
be cancerous, and endometriotic. While most ovarian cysts are non-
cancerous, they can be a contributing factor of infertility and also bring down
the quality of the eggs.
An Ovarian Cystectomy is the surgical removal of ovarian cysts, while
preserving the ovary.
What happens during the procedure?
The procedure is performed through laparoscopy (keyhole) or laparotomy (larger abdominal incision), under anaesthesia. The latter is often recommended when there is a suspicion of cancer, as it offers the specialist a good view of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
If the cysts are non cancerous, they are carefully removed, leaving the ovary
intact. However, if cancer is found, one or both the ovaries may be removed.
After the Laparoscopy procedure, you would need to avoid strenuous activity
for atleast a week. If you have had a laparotomy, you would need to remain in
hospital for about 4 days, and can resume normal activities in a couple of
weeks.
Endometriosis is a condition where the cells that form the lining of the uterus grow into the surrounding areas. Aside from pain, especially during menstruation, during and after intercourse, it can also cause infertility.
About a third of all cases of female infertility are caused by endometriosis where the excess cells occur in the fallopian tubes and block the egg’s passage, or they occur in the ovaries and prevent the release of the egg, or they form in the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes and prevent the transfer of the egg to the tube.
Endometriosis is usually treated in one if three ways: watchful waiting, hormone therapy and surgery. Our specialist makes this call depending on your symptoms, age, severity and if fertility is a factor.
What happens during surgery?
The purpose of surgery is to remove as many endometrial implants and cysts as possible, which would relieve pain and improve fertility, and is recommended for women who are still in the child bearing age. It can be done via laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Laparoscopy is the gold standard and preferred method for endometriosis surgery. During the procedure, which is done under general anaesthesia, several tiny incisions are made through which the laparoscope is inserted to give the surgeon a view of your pelvic organs. The specialist then removes the implants and scar tissue using heat. This is a day care procedure, and you do not need to stay in hospital overnight. Recovery usually takes a 1 -2 weeks.
In a Laparotomy, which is only considered in cases of severe endometriosis, the specialist accesses your reproductive organs through a large incision across your abdomen. This is a much more invasive method, and requires that you remain in hospital for several days.
For women who have already had children and have severe endometriosis, there is a third option: hysterectomy to remove the uterus. In most cases the ovaries are not removed, so while your period stops, you will not go into menopause. A Hysterectomy is usually performed through minimally invasive surgery, or in rare cases, open surgery.
Infertility and pelvic pain can sometimes be caused by scar tissue that joins two surfaces that are usually separate, causing the organs it attaches to become twisted or to move from their normal positions. The adhesions may present as thin sheets of tissue or thick fibrous bands. Adhesiolysis is the surgical procedure to remove or divide this tissue and restore normal position and function to the organs involved.
What happens during the procedure?
The procedure is done through laparoscopic methods (with a tiny incision) and takes between 2 – 4 hours depending of the type and extent of the adhesions. It is done under general anaesthesia and you would have to stay overnight at the hospital after the procedure. You can resume normal activities in a week’s time.